
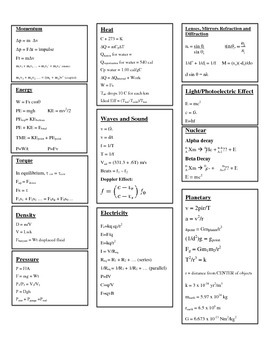
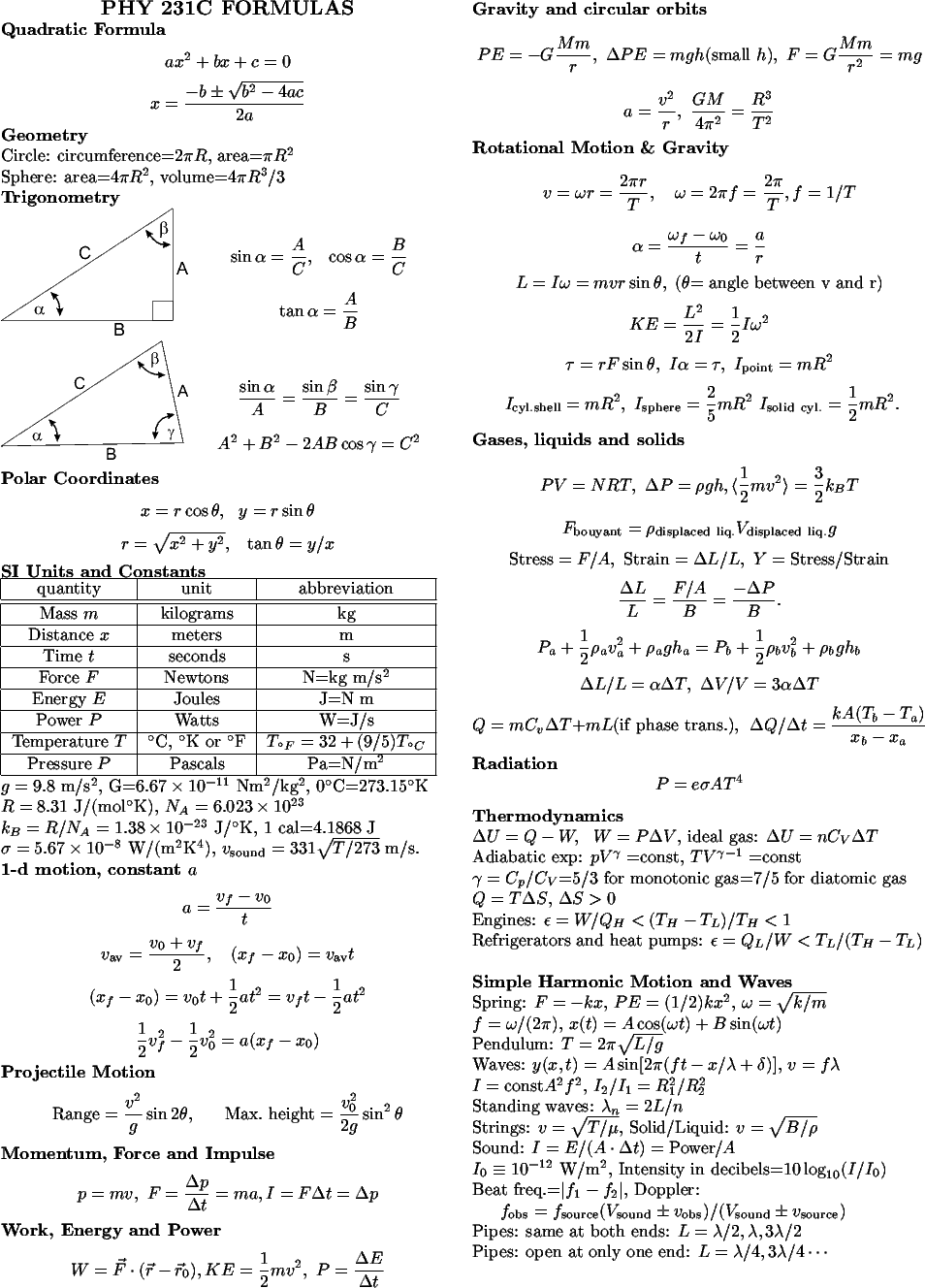
Also, it can be defined as a mass of 5.0188 x 1025 atoms of carbon-12.ġ second is defined as the time in which a cesium atom vibrates 9192631770 times in an atomic clock.ġ kelvin is defined as the temperature at which (1/273.16) is part of the thermodynamics temperature of the triple point of water.ġ candela is (1/60) luminous intensity of an ideal source by an area of cm’ when the source is at the melting point of platinum (1760☌).ġ ampere is the current which is maintained in two straight parallel conductors of infinite length and almost negligible cross-section area placed one meter apart in a vacuum and producing force of a force 2 x 10-7 N per meter length between them.ġ mole is defined as the amount of substance of a system that contains as many as elementary entities ( atoms, molecules, ions, electrons or group of particles, as this and atoms in 0.012 kg of carbon isotope 6C12.Įarlier there were three different systems of units that were used in different countries. These have been defined asġ meter is defined as the distance that contains 1650763.73 wavelengths of orange-red light of atom Kr-8.ġ kilogram is defined in terms of a cylindrical prototype of mass made of platinum and iridium alloys of height 39 mm and diameter 39 mm.

Unit of Fundamental and Supplementary Physical Quantities in SI System Definitions of Fundamental Units For example, units of velocity, force are m/s and kgm/s2 respectively and they are examples of derived units. All those physical quantities which can be expressed in terms of basic physical quantities or are derived from the combination of two or more fundamental quantities are termed as the derived physical quantities. Mass, Length, and Time expressed in kilogram, meter and second respectively are fundamental units. The units used to express these fundamental physical quantities are called fundamental units. Thus fundamental quantities are known as basic physical quantities. In other words, these cannot be resolved further in terms of any other physical quantity. Where 6 is a numerical value and m (meter) is a unit of length.įundamental and Derived Physical Quantitiesįundamental quantities are those elementary physical quantities that do not require any other physical quantity to express them. Measured physical quantity = Numerical value x Unitįor example, the Length of any given rod = 6 m Thus to express any measurement done, we need the numerical value (n) and the unit (μ) of it. The physical quantities are measured in terms of the unit and are known as a standard of that physical quantity. Other similar quantities can also be expressed in terms of these units and can be measured accordingly. Thus, to measure each of the standard quantities, we choose certain units for them that are accepted worldwide. The process of measurement is required to measure or compare physical quantities in day-to-day life.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
